
What Is Classical Conditioning Theory?
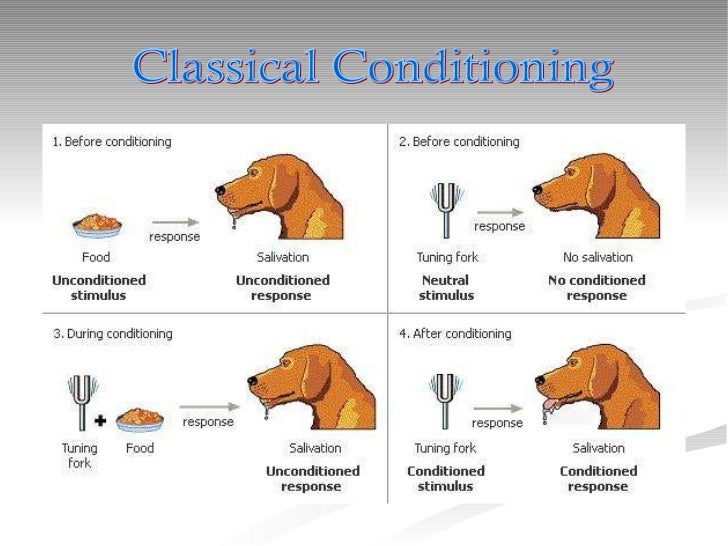
Pavlovian conditioning, also called Classical Conditioning, a type of conditioned learning which occurs because of the subject’s instinctive responses, as opposed to operant conditioning, which is contingent on the willful actions of the subject. It was developed by the Russian physiologist Ivan Petrovich Pavlov (q.v.). See also conditioning · Several types of learning exist. The most basic form is associative learning, i.e., making a new association between events in the environment [1]. There are two forms of associative learning: classical conditioning (made famous by Ivan Pavlov’s experiments with dogs) and operant conditioning. Pavlov’s Dogs · The Pavlovian theory is based on learned responses. This is the step in the process where unconditioned responses to the stimuli get repeated and become learned responses. The next stage is where a response to an unconditioned or conditioned stimulus becomes conditioned. 3. After Conditioning
Related Posts
Pavlovian conditioning, also called Classical Conditioning, a type of conditioned learning which occurs because of the subject’s instinctive responses, as opposed to operant conditioning, which is contingent on the willful actions of the subject. It was developed by the Russian physiologist Ivan Petrovich Pavlov (q.v.). See also conditioning · Several types of learning exist. The most basic form is associative learning, i.e., making a new association between events in the environment [1]. There are two forms of associative learning: classical conditioning (made famous by Ivan Pavlov’s experiments with dogs) and operant conditioning. Pavlov’s Dogs · The Pavlovian theory is based on learned responses. This is the step in the process where unconditioned responses to the stimuli get repeated and become learned responses. The next stage is where a response to an unconditioned or conditioned stimulus becomes conditioned. 3. After Conditioning
Explain the Pavlovian learning model of Consumer Behavior
Pavlovian conditioning, also called Classical Conditioning, a type of conditioned learning which occurs because of the subject’s instinctive responses, as opposed to operant conditioning, which is contingent on the willful actions of the subject. It was developed by the Russian physiologist Ivan Petrovich Pavlov (q.v.). See also conditioning · Several types of learning exist. The most basic form is associative learning, i.e., making a new association between events in the environment [1]. There are two forms of associative learning: classical conditioning (made famous by Ivan Pavlov’s experiments with dogs) and operant conditioning. Pavlov’s Dogs · The Pavlovian theory is based on learned responses. This is the step in the process where unconditioned responses to the stimuli get repeated and become learned responses. The next stage is where a response to an unconditioned or conditioned stimulus becomes conditioned. 3. After Conditioning
Pavlovian Model of Consumer Behaviour
· Several types of learning exist. The most basic form is associative learning, i.e., making a new association between events in the environment [1]. There are two forms of associative learning: classical conditioning (made famous by Ivan Pavlov’s experiments with dogs) and operant conditioning. Pavlov’s Dogs · The Pavlovian theory is based on learned responses. This is the step in the process where unconditioned responses to the stimuli get repeated and become learned responses. The next stage is where a response to an unconditioned or conditioned stimulus becomes conditioned. 3. After Conditioning Pavlovian conditioning, also called Classical Conditioning, a type of conditioned learning which occurs because of the subject’s instinctive responses, as opposed to operant conditioning, which is contingent on the willful actions of the subject. It was developed by the Russian physiologist Ivan Petrovich Pavlov (q.v.). See also conditioning

Post Pagination
· Several types of learning exist. The most basic form is associative learning, i.e., making a new association between events in the environment [1]. There are two forms of associative learning: classical conditioning (made famous by Ivan Pavlov’s experiments with dogs) and operant conditioning. Pavlov’s Dogs · The Pavlovian theory is based on learned responses. This is the step in the process where unconditioned responses to the stimuli get repeated and become learned responses. The next stage is where a response to an unconditioned or conditioned stimulus becomes conditioned. 3. After Conditioning Pavlovian conditioning, also called Classical Conditioning, a type of conditioned learning which occurs because of the subject’s instinctive responses, as opposed to operant conditioning, which is contingent on the willful actions of the subject. It was developed by the Russian physiologist Ivan Petrovich Pavlov (q.v.). See also conditioning
No comments:
Post a Comment